Industry
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
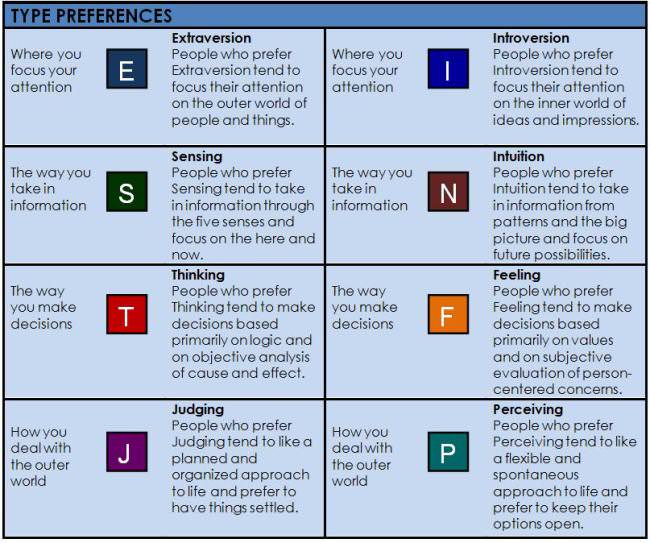
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is used widely to try to classify personally traits based on Carl Jung’s work on psychological typology. Many psychologists do not agree that the MBTI provides a reliable assessment of personality. Nevertheless, the Myers-Briggs personality test is taken by around two million people per year through 10,000 private companies, 2,500 colleges, and 200 government agencies in the United States.[1] The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator tries to classify people into one of 16 personality types. The MBTI test uses four traits which have two complementary aspects to arrive at the 16 classifications.
According to Myers-Briggs, a person who turns to others to increase energy is an Extrovert (E), whereas those who turn inward are Introverts (I). Those who acquire information in a creative way are Intuitive (N), whereas those who take in information pragmatically are Sensing (S). People who make decisions seeking harmony areFeeling (F), but those seeking objective truth are classified as Thinking (T). Persons preferring to act and get closure are Judging (J), whereas those who stay open and adapt are Perceiving (P). Using these categories, a person who is extroverted, intuitive, feeling and judging would be classified as an ENFJ personality. The following chart has summarizes the characteristics of the 16 personality types.
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| INFP | Idealistic, curious and loyal. Seeks to understand others, but can be less accepting of those who threaten core values. |
| INFJ | Insightful and oriented toward the future. Conscientious, but can be firmly decisive to accomplish vision. |
| INTJ | Hold self and others to high standards. Individualistic and visionary, but with a tendency toward skepticism. |
| INTP | Rational, contemplative problem solver. Great tendency to be critical. |
| ISTP | Tolerant and candid. Spends a lot of time silently observing, and provides solutions quickly. |
| ISTJ | Steadfast and hard-working with a practical outlook. Strong need for order and organization. |
| ISFJ | Careful and considerate. Remembers small details about people and objects, and can be very thorough. |
| ISFP | Avoids conflicts and quietly friendly. Open-minded and sympathetic, but prefers to work without others. |
| ESFP | Likes group interaction. Matches common sense with flexibility. Loves people and life, but can be too materialistic. |
| ESFJ | Outgoing and loyal. Follows through on projects, but seeks affirmation and appreciation. |
| ESTJ | Decisive and efficient. Uses systematic approach to problems, and can be forceful in implementing decisions. |
| ESTP | Bold and tactical, with great energy for solving problems. Has difficulty focusing on concepts and theories. |
| ENTP | Clever and entrepreneurial. Dislikes routine. Has difficulty committing to long-term interests. |
| ENTJ | Assumes leadership roles and solves organizational problems. Can be aggressive when putting ideas forward. |
| ENFJ | Goal-oriented and caring. Highly empathetic and very sensitive to criticism. |
| ENFP | Charismatic, imaginative and warm. Needs a lot of affirmation from others, but can also be very supportive. |